
Spot welding: stack the molded parts that need to be welded flush, no need to prepare welding points in advance, and no lead angle. Pass the tip of the welding head through the upper plate to the lower part and plasticize the plastic in the two parts. The resulting melts gather in the dividing seams and form local point connections there.

Ultrasonic flanging: In metal processing, plastic molds can be flanged. In this way, plastic parts and plastic parts and combinations of different types of materials can be linked. According to different tasks, in order to plasticize and form edges, pins and other fixtures, the welding head needs to form the contour of the product on the workbench.

Riveting: Ultrasonic riveting can quickly and cleanly connect thermoplastics and metal or non-weldable parts. This eliminates the need for additional connecting elements. The heat generated during the riveting process can be quickly discharged through the air-cooled welding head. After the basic riveting process, the system will completely solidify the melt under static pressure within the default holding time. This way avoids the occurrence of rebound and realizes seamless connection.
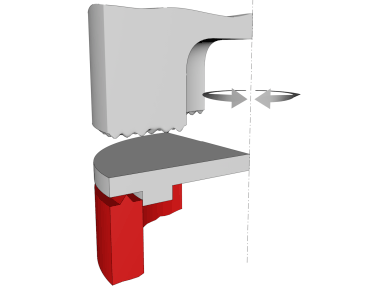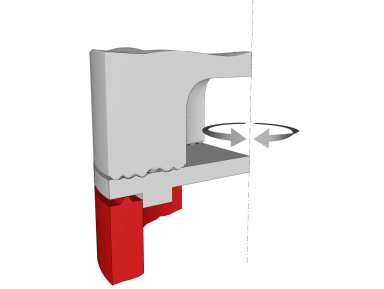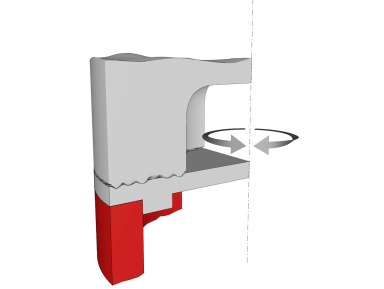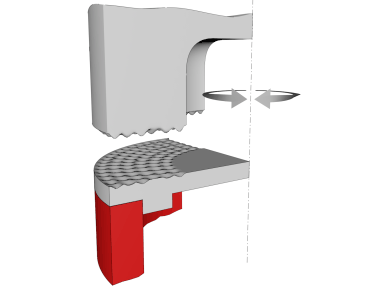
Torsion welding: The structure of this system is still a conventional vertical type, but its process is completely different. This process is a kind of high frequency friction welding. Vibration proceeds along the tangential direction: the welding head causes the upper part to be horizontally displaced relative to the lower part. Under the combined action of high vibration frequency (20 KHz), amplitude and pressure, mutual friction causes a melt between the two workpieces. This method can also be used to combine different plastics.

Embedded metal parts: threaded joints, threaded pins and other metal parts can be embedded in thermoplastics with ultrasonic waves. According to the size and shape of metal parts, its torsional strength and stability can be achieved. The height difference between the embedding levels allows many welding heads to embed multiple parts in one operation. The lower welding head must be adapted to varying degrees of adjustment.

Carton (beverage): Ultrasonic sealing can effectively meet the packaging and sealing needs of all coated carton materials.